Laser cutting machines are advanced sheet metal processing equipment in the industry. In the actual production process, the cutting method directly determines the production efficiency and workpiece quality. Therefore, effective cutting techniques are explored to improve production efficiency and product quality and reduce sheet metal waste rate.
This article shares several cutting techniques that have been verified in practice, including frog jumping, concentrated perforation, automatic focusing, automatic edge finding, common edge cutting, bridge position (micro connection) functions, and analysis of deformation of small holes during laser cutting. In actual production, the above methods can effectively improve the cutting quality and processing efficiency of workpieces.
Frog jump function
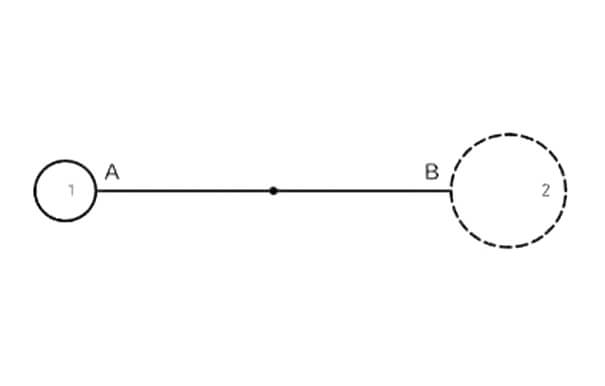
Leapfrog is the idle stroke mode of the laser cutting machine. As shown in the figure, after the cutting process completes hole 1, hole 2 will be cut next. At this time, the cutting head needs to move from point A to point B. Of course, the laser should be turned off during the movement. The movement process from point A to point B is called an idle stroke when the equipment runs "idly".
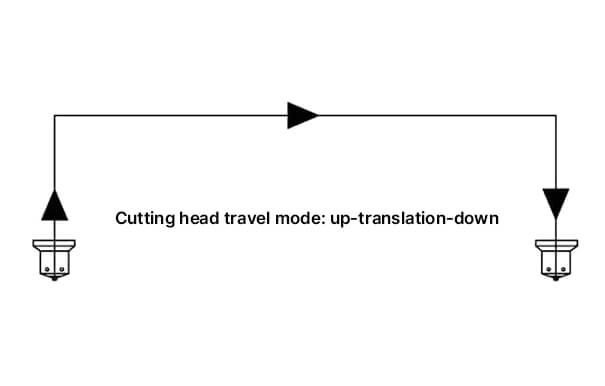
The general idle stroke of the laser cutting machine is shown in the figure. The cutting head must complete three actions in sequence: rise (to a safe enough height), horizontal movement (reaching the top of point B), and fall.
Compressing the idle time can significantly improve the efficiency of the equipment. If the three actions that are completed in sequence are completed "simultaneously", the idle time can be shortened, that is, when the cutting head moves from point A to point B, it rises at the same time; when it approaches point B, it falls at the same time. The trajectory of the cutting head's idle motion is like an arc drawn by a frog jumping.
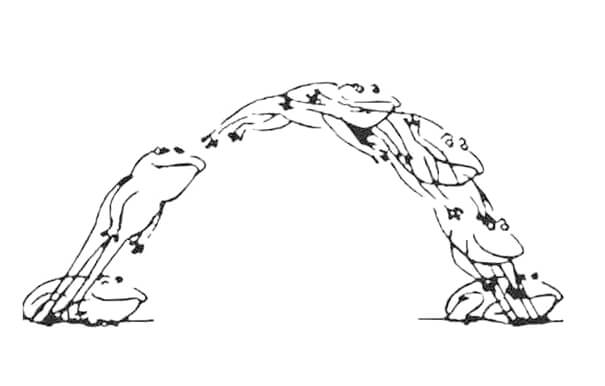
In the development of laser cutting machines, frog jumping is an outstanding technological advancement. The frog jumping action only takes up the time of moving horizontally from point A to point B, saving the time of rising and falling. A frog jumps and catches food; the frog jump of the laser cutting machine "captures" high efficiency. If the laser cutting machine does not have the frog jumping function now, it is probably not in the mainstream.
Centralized perforation process
Centralized perforation, also known as pre-perforation, is a processing technology, not a function of the machine itself. General laser cutting equipment does not have this function. When laser cutting thicker plates, each contour cutting process must go through two stages: perforation and cutting. The conventional processing technology is perforation → cutting contour 1 → perforation → cutting contour 2, as shown in the figure, where the small dots are perforation points and the arrows are the cutting path sequence.
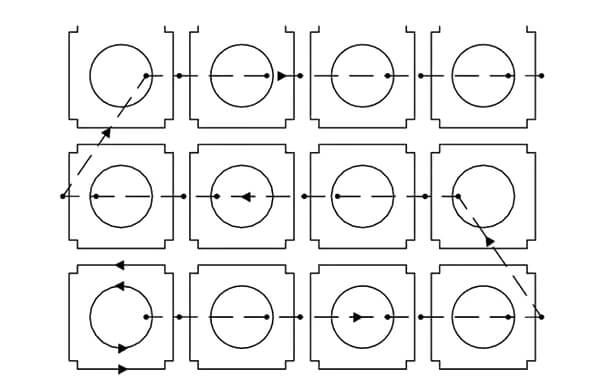
The so-called centralized punching is to execute all the punching processes on the entire sheet in advance, and then execute the cutting process, as shown in the figure, the small dots in the figure are the punching points, and the arrows are the order of the empty stroke path.
The processing route of centralized perforation is to complete the perforation of all contours → return to the starting point → cut all contours. Compared with conventional processing technology, the total length of the equipment's running track increases during centralized perforation, but its advantage is that centralized perforation can effectively avoid overburning. Especially in the process of thick plate perforation, heat accumulates around the perforation point. If cutting is carried out immediately at this time, overburning will occur. With the centralized perforation process, all perforations are completed, and then the starting point is returned to cut. Since there is sufficient time for heat dissipation, overburning is avoided.

Auto focus function
When cutting different materials, the focus of the laser beam is required to fall on different positions of the workpiece cross section. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the position of the focus (focusing). Early laser cutting machines generally used manual focusing; now, many manufacturers' machines have achieved automatic focusing.
Some people may say that it is enough to change the height of the cutting head. When the cutting head is raised, the focus position is high, and when the cutting head is lowered, the focus position is low. It is not that simple.
In fact, during the cutting process, the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece (nozzle height) is about 0.5 to 1.5 mm, which can be regarded as a fixed value, that is, the nozzle height does not change, so the focus cannot be adjusted by raising and lowering the cutting head (otherwise the cutting process cannot be completed).
The focal length of the focusing mirror cannot be changed, so it cannot be expected to focus by changing the focal length. If the position of the focusing mirror is changed, the focus position can be changed: when the focusing mirror is lowered, the focus is lowered, and when the focusing mirror is raised, the focus is raised. ——This is indeed a way of focusing. Automatic focusing can be achieved by using a motor to drive the focusing mirror to move up and down.
Another method of automatic focusing is to place a variable curvature reflector (or adjustable mirror) before the light beam enters the focusing mirror. By changing the curvature of the reflector, the divergence angle of the reflected light beam is changed, thereby changing the focal position.
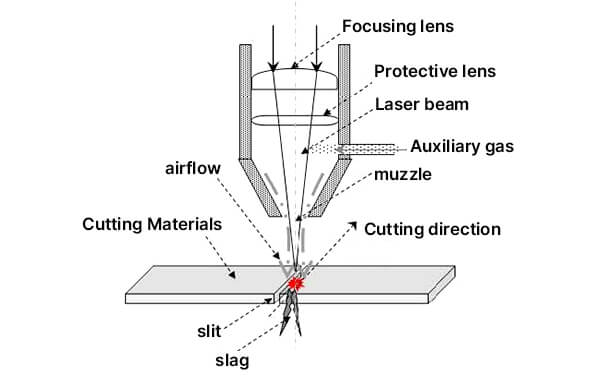
With the automatic focusing function, the processing efficiency of the laser cutting machine can be significantly improved: the punching time of thick plates is greatly reduced; when processing workpieces of different materials and thicknesses, the machine can automatically adjust the focus to the most suitable position quickly.
Automatic edge finding function
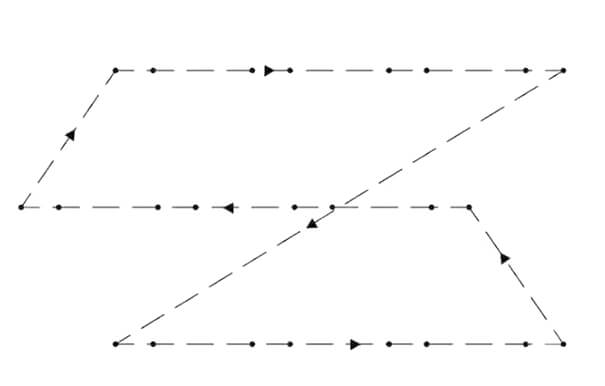
As shown in the figure below, when the sheet is placed on the workbench, if it is skewed, it may cause waste during cutting. If the inclination angle and origin of the sheet can be sensed, the cutting process can be adjusted to suit the angle and position of the sheet, thereby avoiding waste. The automatic edge finding function came into being.
After starting the automatic edge finding function, the cutting head starts from point P and automatically measures 3 points on the two vertical edges of the sheet: P1, P2, and P3, and automatically calculates the inclination angle A of the sheet and the origin of the sheet based on this.
With the help of the automatic edge finding function, the time for adjusting the workpiece earlier is saved - it is not easy to adjust (move) a workpiece weighing hundreds of kilograms on the cutting table, which improves the efficiency of the machine.
A high-power laser cutting machine with advanced technology and powerful functions is a complex system integrating light, machinery, and electricity. The subtleties often hide mysteries. Let us peek into its mysteries together.
Common edge cutting process
If the contours of adjacent parts are straight lines and have the same angle, they can be combined into one straight line and cut only once. This is called common edge cutting. Obviously, common edge cutting reduces the cutting length and can significantly improve processing efficiency.
Common edge cutting does not require the shape of the part to be a rectangle. As shown in the figure below.
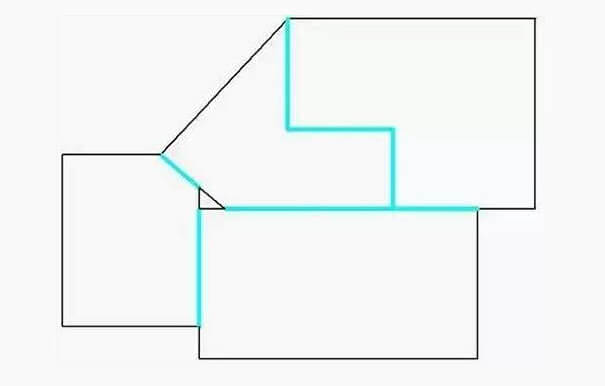
The sky blue lines are common edges. Cutting the common edges not only saves cutting time, but also reduces the number of punching times. Therefore, the benefits are very obvious.
Bridge (micro-connection) cutting process
During laser cutting, the sheet is supported by the serrated support bars. If the cut parts are not small enough, they cannot fall through the gaps of the support bars; if they are not large enough, they cannot be supported by the support bars, and the workpiece may lose balance and tilt. The high-speed cutting head may collide with them, causing the machine to stop at best or even be damaged.
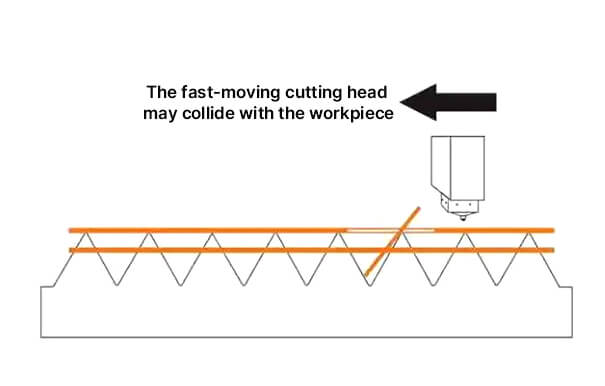
Using the bridge position (micro-connection) cutting process can avoid such problems. Specific method: When programming the laser cutting of the graphics, the closed contour is intentionally disconnected at several locations so that the parts are adhered to the surrounding materials after cutting and do not fall off. These disconnections are called micro-connections. The disconnection distance is about 0.2 to 1 mm and needs to be selected according to the principle that the disconnection distance is inversely proportional to the thickness of the sheet.
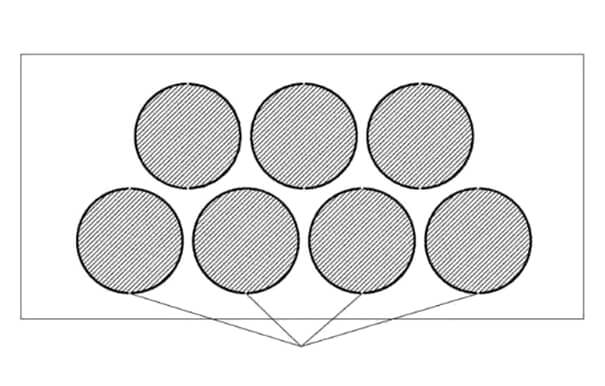
When using micro-joints to connect parts to surrounding materials during the laser cutting process, it is necessary to add an appropriate number of micro-joints based on the length of the contour; it is also necessary to distinguish between the inner and outer contours, so that the inner contour without micro-joints (waste material) falls off, while the outer contour with micro-joints (workpiece) adheres to the parent material, thus eliminating the need for sorting.
Analysis of deformation of cutting small holes
Generally, the size of the cutting hole is specified in the following four cases: (1) When cutting carbon steel plates within 8 mm, the hole diameter cannot be less than the thickness of the plate. (2) When cutting carbon steel plates within 10 mm, the hole diameter cannot be less than 1.2 times the thickness of the plate. (3) When cutting stainless steel plates within 4 mm, the hole diameter cannot be less than the thickness of the plate. (4) When cutting stainless steel plates larger than 4 mm, the hole diameter cannot be less than 1.2 times the thickness of the plate.
In laser cutting production, workpieces with hole diameters smaller than the plate thickness are often encountered, and processing is difficult and the cutting quality is poor. This is mainly because when the program cuts a round hole with a diameter smaller than the plate thickness, the default cutting mode of the machine tool changes from the original continuous cutting to pulse perforation cutting, which makes the laser energy too concentrated in a very small area, and the non-processing area is also burned, causing the hole to deform and affecting the processing quality.
After exploration and trial, we found that if melting cutting is used instead of flame cutting, that is, when the program runs to cutting a small round hole, the cutting state is adjusted, and high-pressure nitrogen is used instead of oxygen for cutting. When the small hole is cut, it is changed back to oxygen cutting. The small holes cut by this method have very regular shapes on both the front and back sides, which can meet the qualified requirements, reduce the scrap rate, and improve production efficiency.
In the actual production process, the operation of the laser cutting machine is complex and delicate, and the workpieces are of various types and materials. As the cutting process becomes more and more mature, as long as you can skillfully use various cutting techniques and accumulate experience in constantly solving problems, you can improve the processing and production capabilities of people and equipment.
Sobre nós
A Durmapress é especializada na conceção, fabrico e venda de vários equipamentos de processamento de metal, incluindo máquinas de dobragem, tesouras, punções, máquinas de corte a laser, etc. A empresa foi fundada em 2000. Com anos de experiência e acumulação de tecnologia. DurmaPress tornou-se uma das marcas bem conhecidas na indústria de máquinas de processamento de metal da China.
Contactar-nos
Publicações recentes
Categorias
Siga-nos
Novo vídeo semanal
Contacte-nos para mais informações
Se tiver alguma informação sobre os nossos produtos, contacte-nos e responderemos no prazo de 24 horas.