abstract
Importance of press brakes
press brakes play a key role in modern manufacturing, as they are one of the main pieces of equipment used to bend sheet metal into various shapes. From aerospace to automotive manufacturing, from building structures to appliance production, the press brake is an indispensable tool whose performance and accuracy have a direct impact on product quality and productivity.
The Impact of Shaft Configuration on press brakes
Shaft configuration plays a critical role in the operation of a press brake. Different shaft configurations affect the flexibility, precision and productivity of the machine. With the right axis configuration, a more efficient process and more accurate forming results can be achieved.
2 Definition and Role of Axes

Axes are one of the key components in a press brake used to control the movement of different parts. They control the position and angle of components such as the platen, backstop, etc. by transmitting force and motion to bend and form sheet metal. Each axis bears a specific function, such as controlling the bending angle, adjusting the bending position, etc., which is an important guarantee for the normal operation and accurate processing of the press brake.In a two-axis press brake, the two axes are mainly the x-axis and the y-axis working in coordination with each other.
X-axis
The X-axis usually controls the front and rear positions of the rear stopper (or rear positioner). The backstop is used to position and support the workpiece during the bending process to ensure accuracy and consistency.
y-axis
The Y-axis is associated with the cylinder (or slide) of the press brake and controls the distance the slide moves up and down, i.e. the depth or angle of the bend. Adjusting the position of the Y-axis can control the degree to which the workpiece is bent.
The impact of axis configuration on bending accuracy and efficiency
The axis configuration of the press brake directly affects the accuracy and efficiency of the process. Reasonable axis configuration can improve the accuracy and stability of processing, reduce the workload of the operator, but also to speed up production and improve production efficiency. Different workpieces and processing requirements require different combinations of axis configurations, so the choice of axis configuration is critical to the entire processing.
4-axis press brake
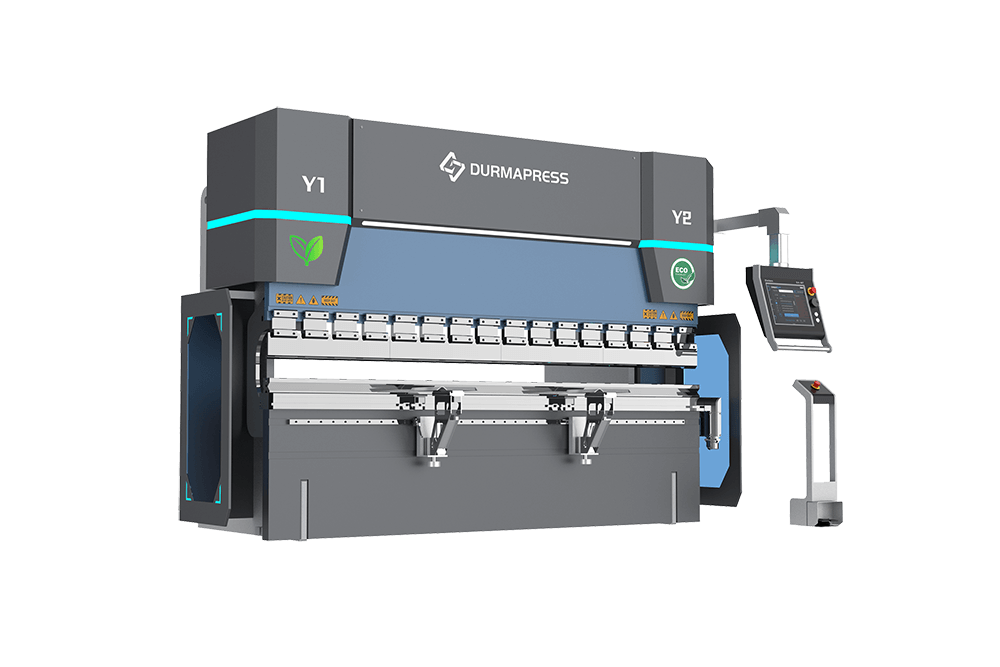
The Impact of Shaft Configuration on press brakes
A 4-axis press brake performs more complex bending of sheet metal by means of four working axes (typically two main axes, top and bottom, and two auxiliary axes). The auxiliary axes provide finer control, allowing the machine to accomplish multiple angles and radii of bending. At the same time, the four axes work in tandem to improve machining accuracy and efficiency, and the roles of each axis are described specifically below.The 4-axis press brake is based on the 2-axis and adds the R-axis and V-axis. V-axis: Usually an additional compensation axis used for fine-tuning during the bending process to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the bending. It may be used to compensate for errors due to material thickness, elasticity, etc.
R-axis
Rotation axis, used to adjust the angle of the workpiece for angle bending or complex shape processing.
V-axis
Usually an additional compensation axis used for fine-tuning during the bending process to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the bending. It may be used to compensate for errors due to material thickness, elasticity, etc.
4-axis press brake in the processing of complex workpiece applications
Usually an additional compensation axis used for fine-tuning during the bending process to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the bending. It may be used to compensate for errors due to material thickness, elasticity, etc.
6-axis press brake
6-axis press brake technical characteristics
6-axis press brake adopts more advanced technology and design, with higher flexibility and processing capacity. In addition to the upper and lower two spindles and four auxiliary axes, it may also include rotary or tilting axes, etc., enabling the machine to accomplish more complex bending shapes. It is based on the 4-axis press brake, mainly adding the V-axis as an additional compensation axis and, for example, the Z1-axis auxiliary axis to accurately control the backstop or other parts of the machine, which helps to better increase the flexibility and accuracy of the bending.
The role of the 6-axis configuration in improving accuracy and efficiency
With finer control and more axes working in tandem, 6-axis press brakes are able to achieve higher machining accuracy, while more complex axis configurations allow the machine to perform more complex bending operations and increase productivity.
6-axis press brake in the high-end manufacturing applications
6-axis press brake in the high-end manufacturing industry, such as precision instruments, electronic products and other fields have a wide range of applications. In precision instrument manufacturing, it is used to manufacture high-precision parts, while in electronic product manufacturing, it is used to manufacture complex metal shells and structural components.
Z1 and Z2 Axes
These axes control the horizontal side-to-side movement of the backstop (or back positioner). The backstop is used to position and support the workpiece during the bending process, ensuring accurate and consistent bending.
8-axis press brake
8-axis press brake represents the latest development trend of bending technology. It adopts advanced control systems, high-precision sensors and intelligent algorithms, which enable the machine to realize automated and intelligent production. At the same time, more axis configurations also enable the machine to accomplish more complex and delicate bending operations. It adds new axes on top of the 6 axes, and the number of axes is more conducive to controlling movement on top of the original.Based on the 6-axis press brake, Y1 Y2 axis is added
Y1 and Y2 Axes
These two axes are usually associated with the slide (or press) of a press brake and are used to control the up and down movement of the slide in the vertical direction to determine the depth or angle of the bend. And in some designs, the Y1 and Y2 axes may control separate slides or be used to provide additional motion flexibility.
conclusion
In conclusion, it is important to understand the different shaft configurations of press brakes to optimize the manufacturing process. Each configuration has its own advantages, from his basic 2-axis system suitable for simple bending tasks to advanced 8-axis setups designed for complex and precise operations.
About Us
Durmapress specializes in designing, manufacturing and selling various metal processing equipment, including bending machines, shears, punches, laser cutting machines, etc. The company was founded in 2000. With years of experience and technology accumulation. DurmaPress has become one of the well-known brands in China's metal processing machinery industry.
Contact Us
Recent Posts
Categories
Follow Us
Weekly New Video
Contact us for more information
If you have any information about our products, please contact us and we will reply within 24 hours.



-300x169.jpg)

